This will be outline of what I read.
What the heck is algorithms?
From dictionary.
Noun
|
Algorithm must be:
1. Well ordered. We must know the correct order to run the instructions
2. Ambiguous Operations. Computers are stupid, the instruction given to them clear enough so they won't be confused.
3. Have effectively computable operations. Again computers are stupid. Operations given to computer must be doable.
4. Produce a result. This is a no-brainer.
5. Halt in finite time. Meaning the instruction have to stop somehow.
The basic operations for sorting algorithms are the comparison operation and the swapping operation.
Comparison operation compared two value and determine which one should come first.
Swapping operation swapped two values. The mechanics of swapping operation is interesting.
Let's say there are two cells, A and B:
_A_ _B_
to swap we would need a temporary cell.
_A_ _TEMP_ _B_
copy the content of A into Temp cell.
_A_ ___A_ _B_
copy the content of B into the original A
_B_ ___A_ _B_
copy the content of A (i.e. the "temp" cell) into B
_B_ ___A_ _A_
discard the one of the A cell (i.e. the "temp" cell)
_B_ _A_
Are you confused?
This is basically what happened.
1. Copy the contents of cell A to temp.
2. Copy the contents of cell B to cell A.
3. Copy the contents of temp to cell B.
The interesting thing about swap operations is that it was combinations of copying operations! In the previous example we copied the operations three times before we could actually swapped the content of the cells. That's neat!
The three types of sorting operations are simple sort, insertion sort and selection sort.
Simple sort works by having a unsorted list of number. Find the smallest number on the unsorted list. Copy the smallest number to a new sorted list. Replaced the position of smallest number with value MAX. Repeat the process until every numbers on the unsorted list is MAX. Then stop To write it in another way, from the tutorial.
Simple Sort Algorithm
- Get a list of unsorted numbers
- Repeat steps 3 through 6 until the unsorted list is empty
- Compare the unsorted numbers
- Select the smallest unsorted number
- Move this number to the sorted list
- Store a maximum value in the place of the smallest number
- Stop
One thing to keep in mind, the maximum value is something that program already have. You don't have figure it out. See the tutorial here and here for more detailed discussions.
Insertion sort works by having a unsorted list of number.
Place a "marker" for the sorted number. Select first unsorted number. Swap this number to the left until it arrives at correct position. Move the "marker" to one position to the right. Repeat this process until there no unsorted number.
Insertion Sort Algorithm
- Get a list of unsorted numbers
- Set a marker for the sorted section after the first number in the list
- Repeat steps 4 through 6 until the unsorted section is empty
- Select the first unsorted number
- Swap this number to the left until it arrives at the correct sorted position
- Advance the marker to the right one position
- Stop

See the tutorial here and here.
Selection sort works by having a list of unsorted number. Set a "marker" at front of unsorted list. Find the smallest number in the unsorted list. Swap this unsorted number with the first number in the sorted position. Advance the "marker" by one position to the right.
Selection Sort Algorithm
- Get a list of unsorted numbers
- Set a marker for the unsorted section at the front of the list
- Repeat steps 4 - 6 until one number remains in the unsorted section
- Compare all unsorted numbers in order to select the smallest one
- Swap this number with the first number in the unsorted section
- Advance the marker to the right one position
- Stop
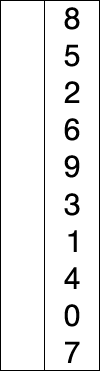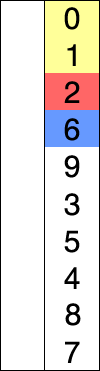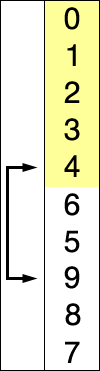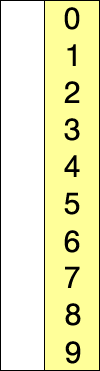
See the tutorial here and here.
| Algorithm | Comparisons | Copies |
| Simple Sort | n * (n-1) | n |
| Insertion Sort | (n-1) + (n-2) + ... + 1 | 3 * [(n-1) + (n-2) + ... + 1] |
| Selection Sort | (n-1) + (n-2) + ... + 1 | 3 * (n-1) |